How much of the variability is contained in the GEM? What are the
errors that occur in predicting T and specific volume anomaly
from hydrography and
IES data by using the GEM assumption? Estimates of these errors are
calculated by comparing the original hydrographic measurements with
the smoothed field. The GEM is divided into bins with dimensions of
100 dbar by 3 milliseconds. The rms error for a bin is defined as the
rms difference between the bin values and all the hydrographic
measurements that fall within the bin.
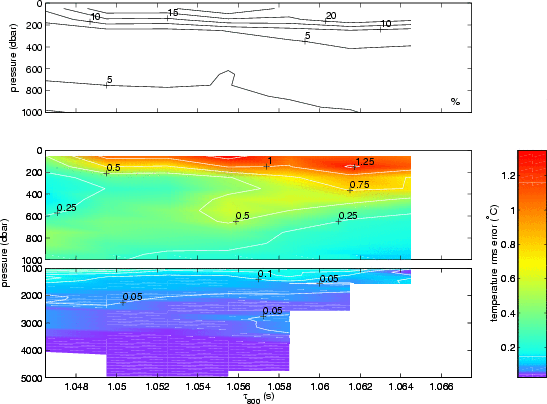
|
|
Error fields for the temperature GEM. The lower two panels are the
rms error determined by subtracting the original hydrographic values
from the smoothed field. The upper panel is the percentage error
calculated by dividing the rms error by the range in T that occurs
at that pressure level, and multiplying by 100. The break between the
lower two panels indicates a change of scale. Contour intervals are
5% (top panel), 0.25°C (middle panel), and 0.05°C
(bottom panel). Blank areas indicate regions where no
hydrographic data were available and extrapolation was used to
calculate the GEM.
|
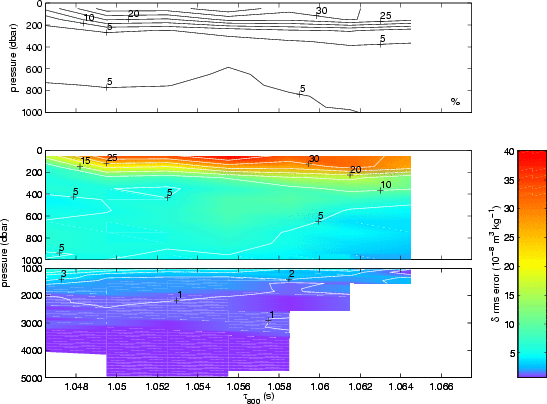
|
|
Error fields for the specific volume anomaly GEM. The lower two
panels are the rms error determined by subtracting the original
hydrographic values from the smoothed field. The upper panel is the
percentage error calculated by dividing the rms error by the range in
specific volume anomaly that occurs at that
pressure level, and multiplying by 100.
The break between the lower two panels indicates a change of scale.
Contour intervals are 5% (top panel), 5x10-8m3/kg
(middle panel), and 1x10-8m3/kg (bottom panel). Blank
areas indicate regions where no hydrographic data were available and
extrapolation was used to calculate the GEM.
|
|



